G'day, fellow Aussies! If you've ever scratched your head over the mysterious STSL tax on your payslip, you're not alone. As a former uni student who's navigated the choppy waters of student loans, I'm here to demystify this often-confusing aspect of our tax system. So, grab a cuppa, and let's dive into the world and find out what is STSL tax!

What is STSL tax?
STSL tax, or Study and Training Support Loans tax, is crucial to Australia’s higher education funding system. It’s the mechanism through which the government ensures that students repay their education loans once they start earning a decent wage, integrated into the broader income tax system.
A Brief History Lesson:
Let's take a quick trip down memory lane. Remember when uni was free? Yeah, neither do I, but our parents might! Back in 1974, the Whitlam government abolished university fees, ushering in an era of free higher education. But this golden age was short-lived.
In 1989, the Hawke government introduced the Higher Education Contribution Scheme (HECS), marking the return of student contributions. HECS was a game-changer designed to make higher education more accessible while ensuring students contributed to the cost.
It started with a uniform charge of about 20% of average course costs. Over the years, HECS evolved, introducing differential rates based on course costs and potential graduate earnings. Fast forward to today, and we have the Study and Training Support Loans (STSL) system, which encompasses HECS-HELP and various other loan programs.
It's all part of the ongoing effort to balance accessibility with sustainability in our higher education system.
Types of Loans Covered by STSL Tax:
The STSL tax umbrella covers several loan programs:
HELP (Higher Education Loan Program)
HELP is the most common loan for university students in Australia. It includes several sub-categories:
- HECS-HELP: For Commonwealth-supported students to cover their student contribution amounts.
- FEE-HELP: For full-fee paying students in higher education courses.
- SA-HELP: To pay for student services and amenities fees.
- OS-HELP: For students studying part of their Australian course overseas.
HELP loans are available to eligible students studying approved courses at universities or other higher education providers. The loan amount is paid directly to the institution, and students only begin repaying once their income reaches a certain threshold. HELP is part of the broader category of study and training loans, which also includes other programs like VET Student Loans and Trade Support Loans.
VET Student Loan (VSL)
VET Student Loans (VSL), also known as vet student loans, are designed for students undertaking vocational education and training. Key features include:
- Available for diploma-level and above qualifications.
- Focuses on courses that address workplace and industry needs.
- Has loan caps that vary depending on the course.
- Requires students to demonstrate academic suitability.
VSL is an evolution of the previous VET FEE-HELP scheme and includes more stringent eligibility criteria to ensure the program’s sustainability.
Student Financial Supplement Scheme (SFSS)
While the SFSS is no longer active for new loans, some Australians still have outstanding debts from this program:
- It was a voluntary loan scheme that operated between 1993 and 2003.
- Allowed students to trade part of their income support payment for a larger, repayable financial supplement.
- Outstanding debts are still being collected through the tax system.
Student Start-up Loan (SSL) and ABSTUDY SSL
These loans are specifically for students receiving certain government allowances:
- Replaces the former Student Start-up Scholarship.
- Available to eligible higher education students receiving Youth Allowance, Austudy, or ABSTUDY Living Allowance.
- Provides financial support for education-related expenses like textbooks and specialised equipment.
- Administered by Services Australia.
Trade Support Loan (TSL)
TSL is tailored for apprentices in designated trades:
- Provides up to $22,890 throughout an apprenticeship (as of 2024).
- Offers a 20% discount on the loan amount upon apprenticeship completion.
- Available in instalments over four years.
- Managed by Australian Apprenticeships Centres and the Department of Employment and Workplace Relations.
TSL aims to support apprentices during their training, particularly in skills shortage areas.
All these loans operate on an income-contingent basis, meaning repayments are only required once the borrower's income reaches a certain threshold. The Australian Taxation Office manages the repayment process through the tax system, ensuring a streamlined loan management and repayment approach.
How STSL Tax Works: The Nitty-Gritty
The Income Threshold
STSL repayments begin when your repayment income reaches a specific minimum repayment threshold. For the 2024-2025 financial year, this threshold is $54,435. It’s important to note that this figure is slightly higher than the $51,550 mentioned in the query, as the most recent data from the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) shows an updated threshold.
What is repayment income?
Your repayment income isn’t just your salary. It includes:
- Your taxable income
- Reportable fringe benefits
- Total net investment losses
- Reportable super contributions
- Exempt foreign employment income
Repayment Rates
Once your repayment income exceeds the threshold, you'll make compulsory repayments. The repayment rate increases progressively with your income. Here's a breakdown of the rates for 2024-2025:
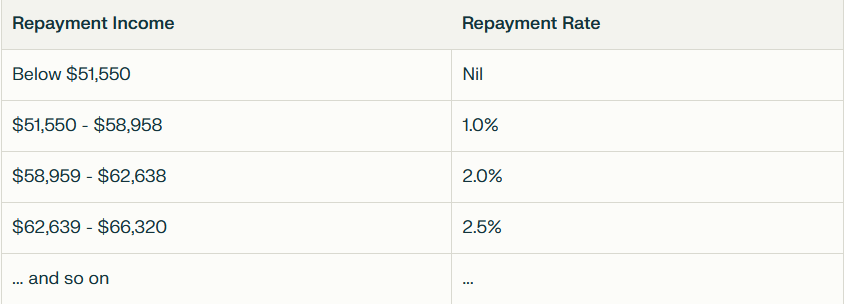
How Repayments Are Calculated
Your repayment amount is calculated by applying the relevant rate to your entire repayment income, not just the portion above the threshold. For example, if your repayment income is $65,000:
- You fall into the 2.0% bracket
- Your repayment would be: $65,000 * 2.0% = $1,300 for the year
The employee's repayment income amount is determined using a specific repayment income calculation method, which takes into account your total repayment income.
Employer Withholding
If you have an STSL debt, your employer will typically withhold additional amounts from your pay to cover your anticipated STSL repayments. This is done through the PAYG withholding system, which is similar to how income tax is deducted from employee's pay now.
Employers are also responsible for withholding additional taxes for other loans like the training support loan.
Annual Reconciliation
When you lodge your tax return, the ATO calculates how much tax is your actual STSL repayment based on your total repayment income for the year. If the amount withheld by your employer is:
- More than required: You'll receive a refund
- Less than required: You'll need to pay the difference
Voluntary Repayments
You can make voluntary repayments at any time to reduce your STSL debt faster. These are in addition to the compulsory repayments and can be made through your myGov account or directly to the ATO.
Overseas Residents
If you move overseas and have an STSL debt, you must still make repayments based on your worldwide income. If you leave Australia for more than 183 days in 12 months, you'll need to lodge an overseas travel notification.

STSL Tax: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly
The Good
- Access to Education: STSL allows many Aussies to pursue higher education who might otherwise not be able to afford it.
- Income-Contingent Repayments: You only start repaying when you can afford to.
- No Interest: Unlike commercial loans, STSL debts are only indexed to inflation.
The Bad
- Reduced Take-Home Pay: Your paycheck takes a hit once you hit the threshold.
- Long-Term Debt: For some, it can take years to repay their STSL debt fully.
The Ugly
- Complexity: The system can be confusing, especially for new graduates.
- Overseas Obligations: If you move abroad, you still need to repay your STSL debt, which can be a hassle.
Managing Your STSL Tax: Tips and Tricks:
Stay Informed
Keeping track of your STSL loan balance is crucial for effective financial planning. The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) provides easy access to this information through your myGov account. By regularly checking your balance, you can:
- Monitor your progress towards repayment
- Identify any discrepancies or errors in your account
- Make informed decisions about voluntary repayments
Consider Voluntary Repayments
Making voluntary repayments can be an effective strategy to clear your STSL debt faster. Here are some key points to consider:
- Voluntary repayments can be made at any time, regardless of your income level.
- These payments are in addition to any compulsory repayments
- There's no minimum amount for voluntary repayments
- Payments made before June 1st of each year can help you avoid indexation on that portion of your debt.
However, it is important to weigh the benefits of early repayment against other financial priorities, such as saving for a home deposit or investing.
Plan for the Threshold
As you approach the STSL repayment threshold, adjusting your budget is crucial. The repayment threshold for the 2024-2025 financial year is $51,550. Here’s what you need to know:
- Once you reach this threshold, repayments start at 1% of your income
- The repayment rate increases progressively with higher income levels
- Understanding these thresholds can help you anticipate changes in your take-home pay
It’s also important to estimate annual repayment income accurately to ensure you meet your repayment obligations.
Understand Salary Packaging
Salary packaging arrangements can have significant implications for your STSL repayments. Here's what you need to be aware of:
- Some salary sacrifice arrangements can reduce your taxable income, potentially lowering your STSL repayments
- However, from July 1st 2017, salary-sacrificed super contributions are included in your STSL repayment income
It's advisable to consult with a financial advisor to understand just how much extra tax on your specific salary packaging arrangement affects your STSL obligations.
The Future of STSL Tax
The STSL system continues to evolve alongside Australia's education landscape. While predicting future changes is challenging, here are some trends to watch:
- Regular adjustments to repayment thresholds and rates to align with economic conditions
- Potential changes in loan programs or consolidation of existing programs
- Ongoing debates about the sustainability and fairness of the current system
While the return of completely free higher education seems unlikely shortly, continued refinement of the STSL system aims to balance accessibility to education with sustainable funding mechanisms.
Remember, while managing your STSL tax can seem daunting, staying informed and proactive can help you navigate the system more effectively and save money in the long run.
Benefits of Choosing the Repayment Income Method over Taxable Earnings for STSL Calculations:
Buffer against additional tax:
The repayment income method can provide a "buffer" to help avoid owing additional tax at the end of the financial year. It is because repayment income includes more components than just taxable gross earnings paid out.
Accounts for other income sources:
The repayment income method considers other income sources beyond just salary and wages, such as reportable fringe benefits, net investment losses, and reportable super contributions. It provides a more comprehensive view of an individual's financial situation.
May result in higher repayments:
For some individuals, calculating STSL on repayment income rather than taxable earnings could result in higher repayments. While this means paying more in the short term, it can help pay down the loan faster.
Aligns with ATO calculations: The repayment income method aligns more closely with how the ATO calculates compulsory repayments at tax time, potentially reducing discrepancies.
Includes exempt foreign income:
The repayment income method includes tax-free foreign employment income, which is not part of taxable earnings. It ensures individuals working overseas still contribute to their loan repayments.
However, it's important to note that the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) advises that STSL should be calculated on taxable earnings. The choice between methods may depend on an individual's specific financial situation and preferences. Some businesses choose the repayment income method to provide a buffer for employees or align more closely with final tax calculations.
In conclusion, while STSL tax might seem like a pain in the wallet, it's an integral part of our education system. It allows Aussies from all walks of life to pursue higher education without the burden of upfront costs. So next time you see that STSL deduction on your payslip, consider it your contribution to a smarter Australia. After all, a little bit of STSL never hurt nobody – except maybe your weekend pub fund!
Frequently Asked Questions:
What happens to my STSL debt if I move overseas?
You're still on the hook, mate. You'll need to make repayments based on your worldwide income.
Can I claim STSL repayments on my tax return?
Unfortunately not. STSL repayments are not tax-deductible.
How long does it take to repay an STSL debt?
How long is a piece of string? It depends on your income and the size of your debt. For some, it might be a few years; for others, it could be a decade or more.
